Respiratory disorders are a critical component of the NCLEX-RN exam, and understanding them is essential for aspiring nurses. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essentials of respiratory disorders, focusing on asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Additionally, we will provide practice scenarios and a mnemonic to help you retain key information.
Understanding Respiratory Disorders
Respiratory disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the lungs and breathing. Two of the most common and significant respiratory disorders are asthma and COPD. Both conditions can severely impact a patient's quality of life and require diligent management and care.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing. These episodes are often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections.
Pathophysiology
Asthma involves three key processes:
- Airway Inflammation: Inflammatory cells infiltrate the airway walls, causing swelling and narrowing.
- Bronchoconstriction: Smooth muscles around the airways tighten, further narrowing the airways.
- Increased Mucus Production: Excess mucus can clog the airways, making breathing difficult.
Clinical Manifestations
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Management
- Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, leukotriene modifiers
- Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants
- Patient Education: Teaching proper inhaler technique and the importance of adherence to treatment
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Pathophysiology
- Chronic Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to mucus production and chronic cough.
- Emphysema: Destruction of the alveoli, reducing the surface area for gas exchange and causing breathlessness.
Clinical Manifestations
- Chronic cough
- Sputum production
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Wheezing
- Frequent respiratory infections
Management
- Medications: Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors
- Oxygen Therapy: For patients with severe hypoxemia
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Exercise training, nutritional advice, and education
- Smoking Cessation: The most crucial step in managing COPD
Practice Scenarios
Scenario 1: Asthma Exacerbation
Patient Profile: A 25-year-old female presents to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness. She has a history of asthma and reports that she ran out of her inhaler medication two days ago.
Assessment Findings:
- Respiratory rate: 30 breaths per minute
- Oxygen saturation: 88% on room air
- Use of accessory muscles for breathing
Nursing Interventions:
- Administer a short-acting beta-agonist (e.g., albuterol) via nebulizer.
- Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation above 92%.
- Assess the patient's peak flow rate and compare it to her personal best.
- Educate the patient on the importance of medication adherence and provide a prescription refill.
Scenario 2: COPD Exacerbation
Patient Profile: A 68-year-old male with a history of COPD presents with increased dyspnea, productive cough with green sputum, and fever. He is a current smoker with a 40-pack-year history.
Assessment Findings:
- Respiratory rate: 28 breaths per minute
- Oxygen saturation: 85% on room air
- Coarse crackles heard on auscultation
Nursing Interventions:
- Administer bronchodilators (e.g., ipratropium) via nebulizer.
- Initiate antibiotics as prescribed for suspected bacterial infection.
- Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation between 88-92%.
- Encourage smoking cessation and refer the patient to a smoking cessation program.
Mnemonic for Respiratory Disorders
To help you remember the key aspects of asthma and COPD, use the mnemonic "ABC DEF":
- A: Airway inflammation (Asthma)
- B: Bronchoconstriction (Asthma)
- C: Chronic cough (COPD)
- D: Dyspnea (Both)
- E: Emphysema (COPD)
- F: Frequent infections (COPD)
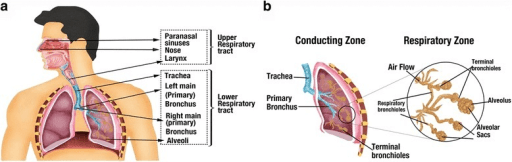
Image Description
The different anatomical divisions of human respiratory system relevant to CF lung disease. Environmental factors such as oxygen and nutrient availability vary significantly in different regions of the human respiratory system and influence disease outcomes. a The airway can be divided primarily into the upper and lower respiratory tract. b Lower respiratory tract is further divided into conductive zone and the respiratory zone. The conducting zones consist of trachea, primary and terminal bronchioles. The conducting zones are secretory in function. The respiratory zones perform the function of air exchange and consist of respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs
Conclusion
Understanding respiratory disorders such as asthma and COPD is crucial for the NCLEX-RN exam and for providing quality patient care. By familiarizing yourself with the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management strategies, you can confidently tackle related questions on the exam. Use the provided practice scenarios to test your knowledge and the mnemonic to aid in retention. Remember, thorough preparation is the key to success on the NCLEX-RN exam.
By mastering the essentials of respiratory disorders, you are one step closer to becoming a competent and compassionate nurse. Good luck with your studies and the NCLEX-RN exam!