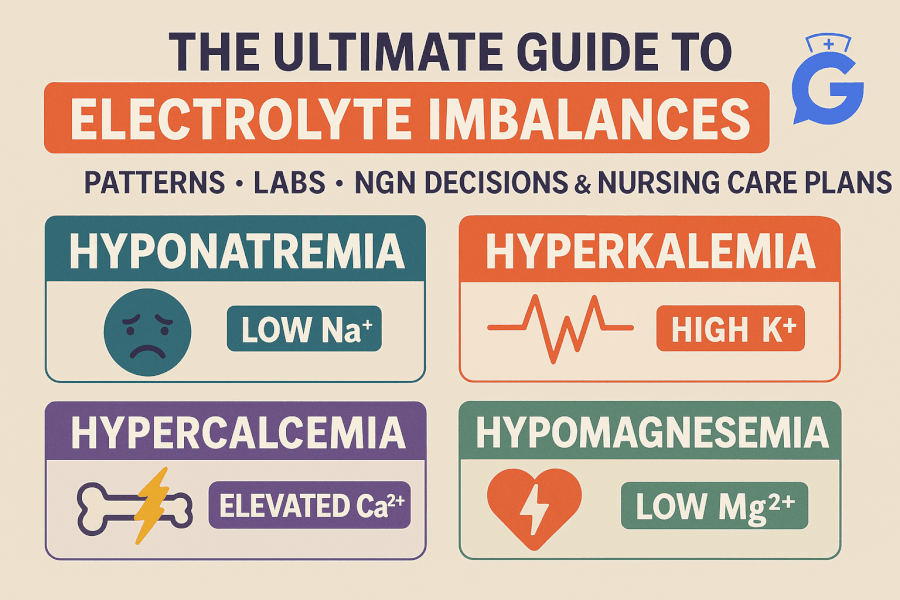
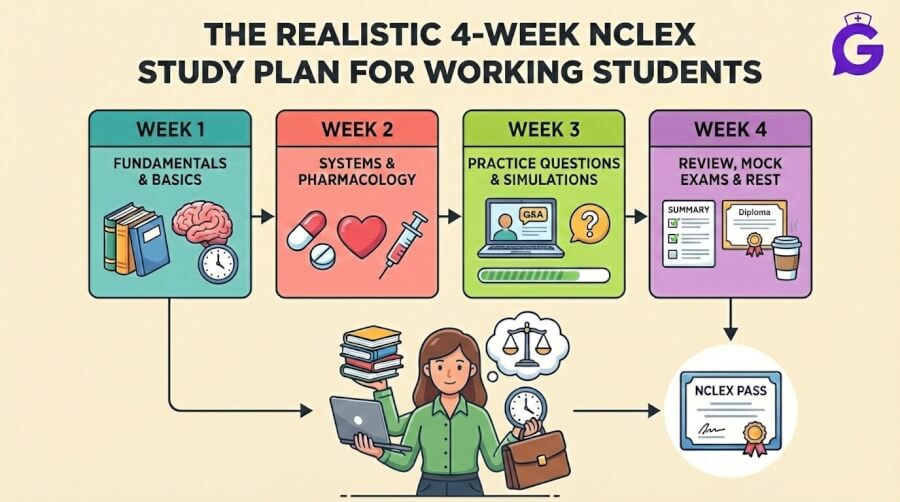
The National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX) is a pivotal step for nursing graduates aiming to become licensed nurses in the United States and Canada. However, with the introduction of the Next Generation NCLEX (NCLEX-GN or NGN), there have been significant changes that aspiring nurses need to be aware of. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective preparation and success. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the seven main differences between the traditional NCLEX and the NCLEX-GN.
1. Exam Format and Structure
Traditional NCLEX:
The traditional NCLEX is a Computerized Adaptive Test (CAT) that adjusts the difficulty of questions based on the test-taker's performance. The exam includes multiple-choice questions, multiple response items, fill-in-the-blank calculations, ordered response items, and hot spot items.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN retains the CAT format but introduces new item types designed to better assess clinical judgment and decision-making skills. These new item types include:
- Extended Multiple Response: More than one correct answer.
- Extended Drag and Drop: Complex ordering and categorization tasks.
- Cloze (Drop-Down): Fill-in-the-blank with multiple options.
- Enhanced Hot Spot: Interactive graphics requiring multiple selections.
2. Focus on Clinical Judgment
Traditional NCLEX:
While the traditional NCLEX assesses a broad range of nursing knowledge and skills, its primary focus is on ensuring that candidates can apply their knowledge safely and effectively in various clinical scenarios.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN places a heightened emphasis on clinical judgment. This shift is in response to the growing complexity of healthcare environments and the need for nurses to make sound clinical decisions. The NGN aims to evaluate a candidate's ability to think critically, prioritize care, and make informed decisions in real-world situations.
3. Case Studies and Realistic Scenarios
Traditional NCLEX:
The traditional NCLEX includes standalone questions that may or may not be related to each other. While some questions are scenario-based, they are often isolated and do not build upon one another.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN incorporates case studies and realistic scenarios that unfold over multiple questions. These case studies require candidates to synthesize information, assess patient needs, and make decisions based on evolving clinical data. This approach mirrors the dynamic nature of actual nursing practice.
4. Length and Time Management
Traditional NCLEX:
The traditional NCLEX-RN exam can have anywhere from 75 to 145 questions, with a maximum time limit of 5 hours. The NCLEX-PN has a similar structure but with a range of 85 to 205 questions.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN maintains a similar range of questions and time limits but introduces more complex question types that may require additional time to answer. Effective time management becomes even more critical as candidates navigate through intricate scenarios and multi-step questions.
5. Preparation and Study Strategies
Traditional NCLEX:
Preparation for the traditional NCLEX often involves a combination of content review, practice questions, and test-taking strategies. Resources such as review books, online courses, and practice exams are commonly used.
NCLEX-GN:
Preparing for the NCLEX-GN requires a more integrated approach. In addition to content review and practice questions, candidates should focus on developing their clinical judgment skills. This can be achieved through simulation exercises, case studies, and interactive learning tools that mimic the NGN's format. Familiarity with the new item types and practicing with them is essential.
6. Scoring and Evaluation
Traditional NCLEX:
The traditional NCLEX uses a pass/fail scoring system based on the candidate's ability to demonstrate minimum competency. The CAT algorithm determines whether the candidate has met the required standard.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN continues to use a pass/fail system but incorporates a more nuanced evaluation of clinical judgment. The scoring algorithm considers the candidate's performance on complex item types and case studies, providing a more comprehensive assessment of their readiness for practice.
7. Feedback and Results
Traditional NCLEX:
Candidates receive their results within a few days to a few weeks after taking the traditional NCLEX. The results indicate whether they have passed or failed, but detailed feedback on specific areas of weakness is limited.
NCLEX-GN:
The NCLEX-GN aims to provide more detailed feedback to candidates, highlighting areas of strength and areas needing improvement. This feedback can be invaluable for those who need to retake the exam or for ongoing professional development.
Conclusion
The transition from the traditional NCLEX to the NCLEX-GN represents a significant evolution in nursing licensure examinations. By focusing on clinical judgment and incorporating realistic scenarios, the NGN aims to better prepare nurses for the complexities of modern healthcare. Understanding these seven main differences is essential for effective preparation and success on the NCLEX-GN. Aspiring nurses should adapt their study strategies to meet the demands of this new exam format, ensuring they are well-equipped to provide high-quality patient care.
By staying informed and prepared, you can navigate the changes and achieve your goal of becoming a licensed nurse. Good luck on your journey to success!