Preparing for the NCLEX can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to mastering the complexities of cardiovascular disorders. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of key cardiovascular conditions, their pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and management strategies. Additionally, we have included 8 challenging NCLEX-style questions with detailed answers to help you test your knowledge and readiness.
Understanding Cardiovascular Disorders
Cardiovascular disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. These disorders can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and may lead to severe complications if not managed properly. Below, we delve into some of the most common cardiovascular disorders you need to know for the NCLEX.
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Pathophysiology: CAD is caused by the buildup of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the myocardium. This can result in angina, myocardial infarction (heart attack), or sudden cardiac death.
Clinical Manifestations:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Palpitations
Diagnostic Tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Stress testing
- Coronary angiography
- Blood tests (e.g., lipid profile, cardiac enzymes)
Management:
- Lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, smoking cessation)
- Medications (e.g., statins, beta-blockers, antiplatelets)
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
2. Heart Failure
Pathophysiology: Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body's needs. It can be classified as systolic or diastolic heart failure, depending on whether the issue is with the heart's contraction or relaxation.
Clinical Manifestations:
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Orthopnea (difficulty breathing while lying flat)
- Edema (swelling, particularly in the lower extremities)
- Fatigue
- Jugular venous distention (JVD)
Diagnostic Tests:
- Echocardiogram
- B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels
- Chest X-ray
- ECG
Management:
- Lifestyle modifications (sodium restriction, fluid management)
- Medications (e.g., ACE inhibitors, diuretics, beta-blockers)
- Device therapy (e.g., implantable cardioverter-defibrillator)
- Heart transplant (in severe cases)
3. Hypertension
Pathophysiology: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic condition where the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high. It can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Clinical Manifestations:
- Often asymptomatic ("silent killer")
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood pressure measurement
- Urinalysis
- Blood tests (e.g., electrolytes, renal function)
- ECG
Management:
- Lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, weight loss)
- Medications (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers)
- Regular monitoring and follow-up
4. Arrhythmias
Pathophysiology: Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can result from issues with the heart's electrical system. They can range from benign to life-threatening.
Clinical Manifestations:
- Palpitations
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Syncope (fainting)
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
Diagnostic Tests:
- ECG
- Holter monitor
- Electrophysiological study (EPS)
- Blood tests (e.g., electrolyte levels)
Management:
- Medications (e.g., antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers)
- Electrical cardioversion
- Catheter ablation
- Implantable devices (e.g., pacemaker, defibrillator)
8 Challenging NCLEX Questions with Answers
Question 1
A patient with a history of coronary artery disease presents with chest pain radiating to the left arm. What is the priority nursing intervention?
A. Administer nitroglycerin sublingually.
B. Obtain a 12-lead ECG.
C. Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
D. Call the healthcare provider.
Answer: C. Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
Rationale: The priority is to ensure adequate oxygenation to the myocardium. Administering oxygen can help reduce myocardial ischemia. After oxygen administration, obtaining an ECG and administering nitroglycerin are also important steps.
Question 2
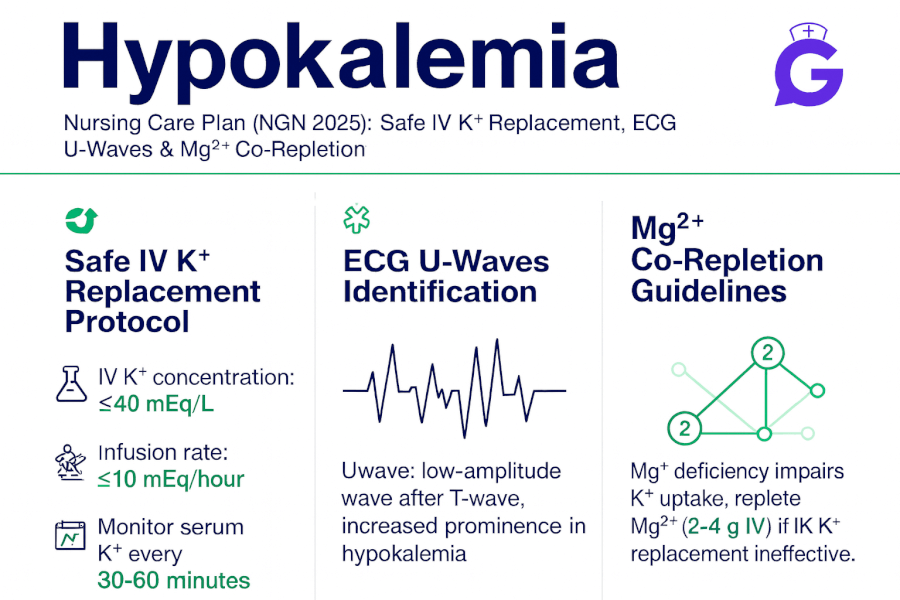
A patient with heart failure is prescribed furosemide. Which electrolyte imbalance should the nurse monitor for?
A. Hyperkalemia
B. Hypokalemia
C. Hypernatremia
D. Hyponatremia
Answer: B. Hypokalemia
Rationale: Furosemide is a loop diuretic that can cause significant potassium loss, leading to hypokalemia. Monitoring potassium levels is crucial to prevent complications.
Question 3
Which lifestyle modification is most important for a patient with hypertension?
A. Increasing dietary potassium
B. Reducing sodium intake
C. Increasing fluid intake
D. Reducing protein intake
Answer: B. Reducing sodium intake
Rationale: Reducing sodium intake is a key lifestyle modification for managing hypertension, as it helps lower blood pressure.
Question 4
A patient with atrial fibrillation is at increased risk for which complication?
A. Myocardial infarction
B. Stroke
C. Heart failure
D. Hypertension
Answer: B. Stroke
Rationale: Atrial fibrillation can lead to the formation of blood clots in the atria, which can travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
Question 5
Which diagnostic test is most definitive for diagnosing heart failure?
A. ECG
B. Chest X-ray
C. Echocardiogram
D. BNP levels
Answer: C. Echocardiogram
Rationale: An echocardiogram provides detailed information about the heart's structure and function, making it the most definitive test for diagnosing heart failure.
Question 6
A patient with a history of myocardial infarction is prescribed aspirin. What is the primary purpose of this medication?
A. To reduce pain
B. To prevent blood clots
C. To lower cholesterol
D. To reduce blood pressure
Answer: B. To prevent blood clots
Rationale: Aspirin is an antiplatelet medication that helps prevent the formation of blood clots, reducing the risk of another myocardial infarction.
Question 7
Which symptom is most indicative of left-sided heart failure?
A. Peripheral edema
B. Jugular venous distention
C. Hepatomegaly
D. Pulmonary congestion
Answer: D. Pulmonary congestion
Rationale: Left-sided heart failure leads to a backup of blood in the lungs, causing pulmonary congestion and symptoms such as dyspnea and orthopnea.
Question 8
A patient with hypertension is started on an ACE inhibitor. Which side effect should the nurse monitor for?
A. Bradycardia
B. Hyperkalemia
C. Hypoglycemia
D. Hypokalemia
Answer: B. Hyperkalemia
Rationale: ACE inhibitors can cause hyperkalemia by reducing aldosterone levels, which leads to potassium retention.
Conclusion
Mastering cardiovascular disorders is crucial for success on the NCLEX and in clinical practice. By understanding the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tests, and management strategies for these conditions, you will be better prepared to provide high-quality care to your patients. Use the challenging questions provided to test your knowledge and identify areas where you may need further study. Good luck with your NCLEX preparation!