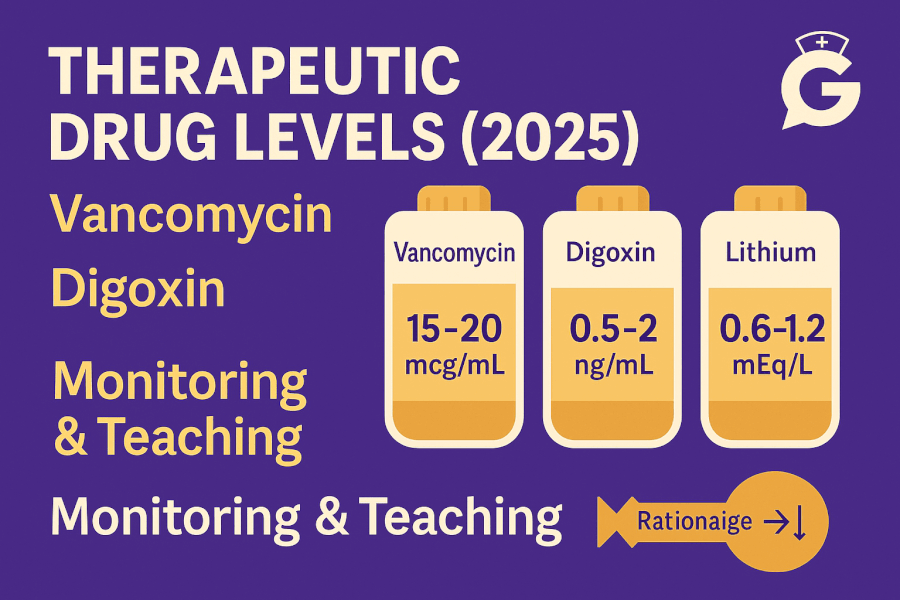
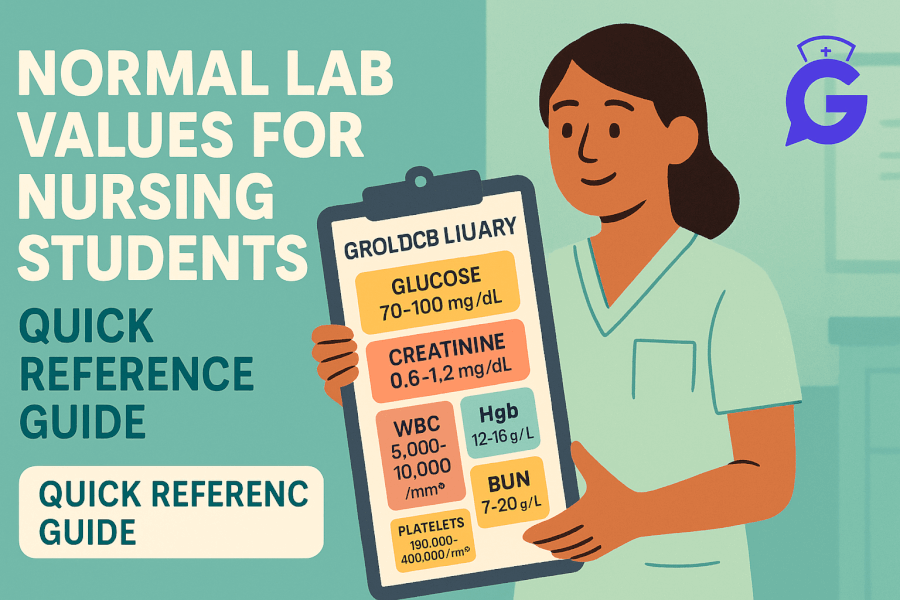
Preparing for the NCLEX can be a daunting task, but understanding key vocabulary can significantly ease the process. The NCLEX (National Council Licensure Examination) is designed to test the knowledge, skills, and abilities essential for safe and effective practice as a newly licensed, entry-level nurse. To help you succeed, we’ve compiled a comprehensive list of 37 essential vocabulary words you must know before taking the NCLEX, complete with examples to illustrate their use in a clinical context.
🎯 Free NCLEX quiz on topics covered in this article!
Test your knowledge after you finish reading.
1. Asepsis
Asepsis refers to the absence of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. It is crucial in preventing infections.
Example: "The nurse practiced asepsis by thoroughly washing her hands before dressing the wound."
2. Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a slower than normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute.
Example: "The patient was diagnosed with bradycardia after the ECG showed a heart rate of 50 beats per minute."
3. Cyanosis
Cyanosis is a bluish discoloration of the skin due to poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood.
Example: "The nurse noticed cyanosis around the patient's lips and immediately administered oxygen."
4. Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis refers to excessive sweating, often a symptom of an underlying condition.
Example: "The patient experienced diaphoresis and chest pain, indicating a possible myocardial infarction."
5. Edema
Edema is the swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues.
Example: "The nurse observed pitting edema in the patient's lower extremities, suggesting heart failure."
6. Febrile
Febrile means having or showing symptoms of a fever.
Example: "The febrile patient was given antipyretics to reduce his temperature."
7. Hematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood, indicating a possible gastrointestinal bleed.
Example: "The patient’s hematemesis required immediate endoscopic evaluation."
8. Hypoxia
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply.
Example: "The patient with COPD was at risk for hypoxia and required continuous monitoring."
9. Iatrogenic
Iatrogenic refers to any condition that is caused by medical treatment or diagnostic procedures.
Example: "The patient developed an iatrogenic infection following surgery."
10. Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes due to high bilirubin levels.
Example: "The newborn was treated for jaundice with phototherapy."
11. Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes characterized by high levels of ketones in the blood.
Example: "The patient with type 1 diabetes was admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis."
12. Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is an increase in the number of white blood cells, often indicating an infection.
Example: "The patient's leukocytosis suggested a bacterial infection."
13. Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort or unease, often the first sign of an infection or other disease.
Example: "The patient reported malaise and fatigue, prompting further diagnostic tests."
14. Nosocomial
Nosocomial refers to infections that are acquired in a hospital setting.
Example: "The patient developed a nosocomial infection during his stay in the ICU."
15. Orthopnea
Orthopnea is difficulty breathing when lying flat, often seen in patients with heart failure.
Example: "The patient with congestive heart failure experienced orthopnea and needed to sleep propped up on pillows."
16. Pallor
Pallor is an unhealthy pale appearance, often due to anemia or shock.
Example: "The nurse noted pallor in the patient, indicating possible blood loss."
17. Quarantine
Quarantine is the isolation of patients to prevent the spread of infectious disease.
Example: "The patient with tuberculosis was placed in quarantine to prevent transmission."
18. Rales
Rales are abnormal lung sounds heard through a stethoscope, often indicating fluid in the lungs.
Example: "The nurse auscultated rales in the patient's lungs, suggesting pulmonary edema."
19. Sepsis
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to an infection.
Example: "The patient was diagnosed with sepsis and required immediate antibiotic therapy."
20. Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a faster than normal heart rate, typically above 100 beats per minute.
Example: "The patient exhibited tachycardia with a heart rate of 120 beats per minute."
21. Urticaria
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin rash triggered by an allergic reaction.
Example: "The patient developed urticaria after receiving the new medication."
22. Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that are visible just under the surface of the skin.
Example: "The patient sought treatment for painful varicose veins in her legs."
23. Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound made while breathing, often associated with asthma or COPD.
Example: "The nurse heard wheezing in the patient's lungs, indicating an asthma exacerbation."
24. Xerostomia
Xerostomia is the medical term for dry mouth, often a side effect of certain medications.
Example: "The patient complained of xerostomia, which was managed by increasing fluid intake."
25. Yawn
Yawning is an involuntary action that involves opening the mouth wide and inhaling deeply, often due to tiredness or boredom.
Example: "The patient’s frequent yawning was noted during the assessment of his sleep patterns."
26. Zoonosis
Zoonosis refers to diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans.
Example: "Rabies is a zoonosis that requires immediate medical attention if exposure is suspected."
27. Anuria
Anuria is the absence of urine production, often indicating kidney failure.
Example: "The patient with anuria was started on dialysis."
28. Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in red blood cells.
Example: "Elevated bilirubin levels in the patient’s bloodwork indicated liver dysfunction."
29. Cystitis
Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder, often caused by a urinary tract infection.
Example: "The patient was treated for cystitis with antibiotics."
30. Dyspnea
Dyspnea is difficult or labored breathing.
Example: "The patient with COPD experienced dyspnea on exertion."
31. Erythema
Erythema is redness of the skin, often a sign of infection or inflammation.
Example: "The nurse noted erythema around the surgical site, indicating possible infection."
32. Fistula
A fistula is an abnormal connection between two body parts, such as organs or blood vessels.
Example: "The patient developed an arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis access."
33. Glucosuria
Glucosuria is the excretion of glucose in the urine, typically a sign of diabetes.
Example: "The patient's glucosuria was confirmed with a urine dipstick test."
34. Hematuria
Hematuria is the presence of blood in the urine.
Example: "The patient’s hematuria required further investigation to rule out kidney stones."
35. Ileus
Ileus is a temporary and often painful lack of movement in the intestines.
Example: "The patient developed an ileus following abdominal surgery."
36. JVD (Jugular Venous Distention)
JVD is the visible bulging of the jugular veins, often a sign of heart failure.
Example: "The nurse observed JVD in the patient, suggesting increased central venous pressure."
37. Kyphosis
Kyphosis is an excessive outward curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back.
Example: "The elderly patient had kyphosis, which affected her posture and mobility."
Conclusion
Mastering these 37 essential vocabulary words will not only help you feel more confident as you prepare for the NCLEX but also enhance your ability to provide high-quality patient care. Understanding these terms and their clinical implications is crucial for any aspiring nurse. Good luck with your studies and on your journey to becoming a licensed nurse!
By familiarizing yourself with these key terms, you’ll be better prepared to tackle the NCLEX and excel in your nursing career. Remember, knowledge is power, and every bit of preparation brings you one step closer to success.