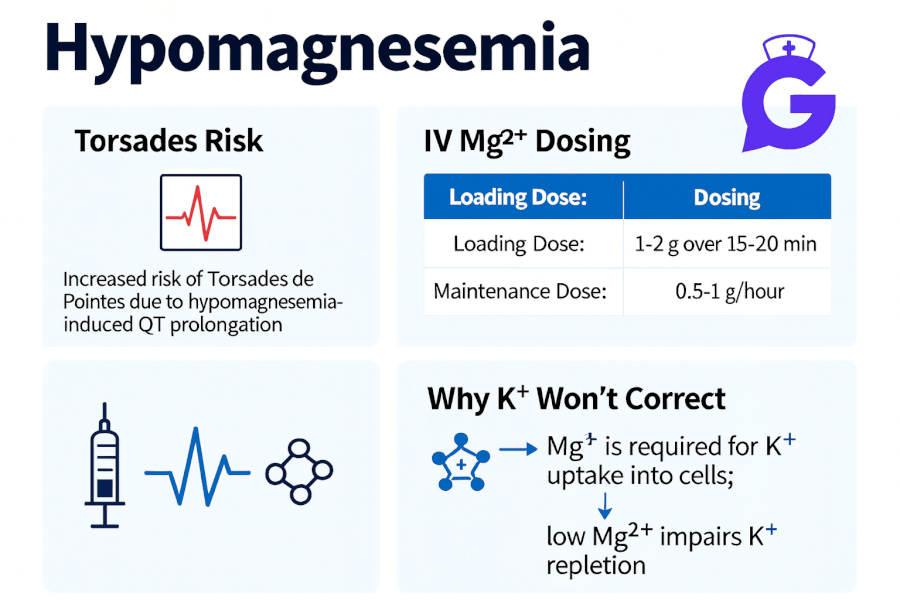
Preparing for the NCLEX exam can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to mastering pharmacology. Understanding medications, their indications, side effects, and uses is crucial for success. This comprehensive guide covers 26 essential medications you need to know for the NCLEX, organized by class, to help you study effectively and efficiently. Looking ahead to updated exam content? Check out must-know NCLEX drugs for 2025 for an updated pharmacology review.
1. Analgesics
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Class: Analgesic, Antipyretic
- Indications: Pain relief, fever reduction
- Side Effects: Hepatotoxicity in high doses, rash
- Use: Commonly used for mild to moderate pain and fever
Morphine
- Class: Opioid Analgesic
- Indications: Severe pain
- Side Effects: Respiratory depression, constipation, nausea
- Use: Management of severe pain, often post-surgical
2. Antibiotics
Amoxicillin
- Class: Penicillin Antibiotic
- Indications: Bacterial infections
- Side Effects: Allergic reactions, gastrointestinal upset
- Use: Treats infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and UTIs
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Class: Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic
- Indications: Bacterial infections
- Side Effects: Tendon rupture, photosensitivity
- Use: Used for UTIs, respiratory infections, and skin infections
3. Anticoagulants
Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Class: Anticoagulant
- Indications: Prevention of blood clots
- Side Effects: Bleeding, bruising
- Use: Long-term anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation, DVT, PE
Heparin
- Class: Anticoagulant
- Indications: Prevention and treatment of blood clots
- Side Effects: Bleeding, thrombocytopenia
- Use: Acute anticoagulation, often used in hospital settings
4. Antidepressants
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
- Class: SSRI Antidepressant
- Indications: Depression, anxiety disorders
- Side Effects: Insomnia, sexual dysfunction, weight changes
- Use: First-line treatment for major depressive disorder
Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Class: SSRI Antidepressant
- Indications: Depression, OCD, PTSD
- Side Effects: Nausea, dizziness, dry mouth
- Use: Commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety disorders
5. Antihypertensives
Lisinopril
- Class: ACE Inhibitor
- Indications: Hypertension, heart failure
- Side Effects: Cough, hyperkalemia, angioedema
- Use: First-line treatment for hypertension
Amlodipine (Norvasc)
- Class: Calcium Channel Blocker
- Indications: Hypertension, angina
- Side Effects: Edema, dizziness, palpitations
- Use: Effective for lowering blood pressure and managing angina
6. Antidiabetics
Metformin (Glucophage)
- Class: Biguanide
- Indications: Type 2 diabetes
- Side Effects: Gastrointestinal upset, lactic acidosis
- Use: First-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, helps control blood sugar levels
Insulin Glargine (Lantus)
- Class: Long-acting Insulin
- Indications: Diabetes mellitus
- Side Effects: Hypoglycemia, weight gain
- Use: Provides basal insulin coverage for diabetes management
7. Antipsychotics
Haloperidol (Haldol)
- Class: Typical Antipsychotic
- Indications: Schizophrenia, acute psychosis
- Side Effects: Extrapyramidal symptoms, sedation
- Use: Management of acute and chronic psychotic disorders
Risperidone (Risperdal)
- Class: Atypical Antipsychotic
- Indications: Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder
- Side Effects: Weight gain, metabolic syndrome
- Use: Treats schizophrenia and bipolar mania
🥇Voted #1 Nursing Study Tool.
Personalized AI Tutor + Instant Answers to All Your Questions. 100% Money Back Guarantee!
8. Anticonvulsants
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
- Class: Anticonvulsant
- Indications: Seizure disorders
- Side Effects: Gingival hyperplasia, ataxia
- Use: Management of tonic-clonic and partial seizures
Valproic Acid (Depakote)
- Class: Anticonvulsant
- Indications: Seizures, bipolar disorder
- Side Effects: Hepatotoxicity, pancreatitis
- Use: Used for seizure control and mood stabilization
9. Bronchodilators
Albuterol (Ventolin)
- Class: Beta-2 Agonist
- Indications: Asthma, COPD
- Side Effects: Tachycardia, tremors
- Use: Quick relief of bronchospasm in asthma and COPD
Ipratropium (Atrovent)
- Class: Anticholinergic
- Indications: COPD
- Side Effects: Dry mouth, cough
- Use: Maintenance therapy for COPD
10. Diuretics
Furosemide (Lasix)
- Class: Loop Diuretic
- Indications: Edema, hypertension
- Side Effects: Hypokalemia, dehydration
- Use: Reduces fluid overload in heart failure and hypertension
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
- Class: Thiazide Diuretic
- Indications: Hypertension, edema
- Side Effects: Hypokalemia, hyperglycemia
- Use: First-line treatment for hypertension
11. Corticosteroids
Prednisone
- Class: Corticosteroid
- Indications: Inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders
- Side Effects: Weight gain, osteoporosis, hyperglycemia
- Use: Reduces inflammation in conditions like asthma and arthritis
Dexamethasone
- Class: Corticosteroid
- Indications: Inflammation, cerebral edema
- Side Effects: Insomnia, mood changes
- Use: Used in cancer therapy and to reduce cerebral edema
12. Antiemetics
Ondansetron (Zofran)
- Class: 5-HT3 Antagonist
- Indications: Nausea, vomiting
- Side Effects: Headache, constipation
- Use: Prevention of nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy and post-surgery
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
- Class: Dopamine Antagonist
- Indications: Nausea, gastroparesis
- Side Effects: Tardive dyskinesia, drowsiness
- Use: Treats nausea and enhances gastric motility
13. Antihistamines
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Class: Antihistamine
- Indications: Allergic reactions, insomnia
- Side Effects: Drowsiness, dry mouth
- Use: Relief of allergy symptoms and as a sleep aid
Loratadine (Claritin)
- Class: Antihistamine
- Indications: Allergic rhinitis
- Side Effects: Headache, fatigue
- Use: Non-drowsy relief of allergy symptoms
Conclusion
Mastering these 26 medications is crucial for any nursing student preparing for the NCLEX exam. Understanding their indications, side effects, and uses will not only help you pass the exam but also ensure you provide safe and effective care in your nursing practice. Use this guide as a foundation for your pharmacology studies and build upon it with additional resources and practice questions. Good luck on your journey to becoming a registered nurse!